Playing Flush and Straight Draws. Mathematics: Flushes & Straights: Simple Pot Odds: Implied Odds: Reverse Implied Odds. Watch SplitSuit's video on Flushes and Flush Draws for 8 hand histories involving strategy on playing flushes in Texas Hold'em. You are on the flop with a pretty decent flush draw. Texas holdem is played with a deck of 52 playing cards, consisting of the same four suits, and 13 ranks in every deck. You know each deck has an ace of spades, and ace of hearts, an ace of clubs, and an ace of diamonds. The same is true for kings, queens, and all of the ranks down through twos.
- Texas Hold'em Straight Odds
- Texas Holdem Tournament Videos
- Texas Hold'em Straight Vs Flush
- Texas Hold'em Straight Tie
On This Page
Introduction
Rules
- A single 52-card deck is used. All cards count as its poker value. Aces may be high or low.
- One player is designated as the dealer, usually with a laminated marker. This person does not have to physically deal the game. However it is important that a symbolic dealer position rotate around the table.
- The player to the dealer's left must make a 'small blind' bet. The player to the left of the small blind must make a 'big blind' bet. The amounts of both blinds should be specified in advance. The purpose of the blinds is to get the ball rolling with some money in the pot.
- Two cards shall be dealt down to each player, starting with the person to the dealer's left.
- The player to the left of the big blind must either call or raise the big blind bet. The play in turn will go around the table according to normal poker rules, which I assume the reader already knows. Table rules will specify any limits on the size or number of allowed raises.
- The small blind may also raise the big blind. If nobody raises the big blind the player making the big blind has the option to raise his own bet. The term for this is the 'big blind option.'
- Three community cards will be dealt face up in the center of the table. This is called the 'flop.'
- Another round of betting will ensue, starting with the player to the dealer's left.
- A fourth community card will be dealt face up in the center of the table. This card is called the 'turn.'
- Another round of betting will ensue, starting with the player to the dealer's left. Generally the minimum bet is double the first two rounds of betting.
- A fifth and final community card will be dealt face up in the center of the table. This card is called the 'river.'
- Another round of betting will ensue, starting with the player to the dealer's left. The minimum bet is generally the same as the previous round.
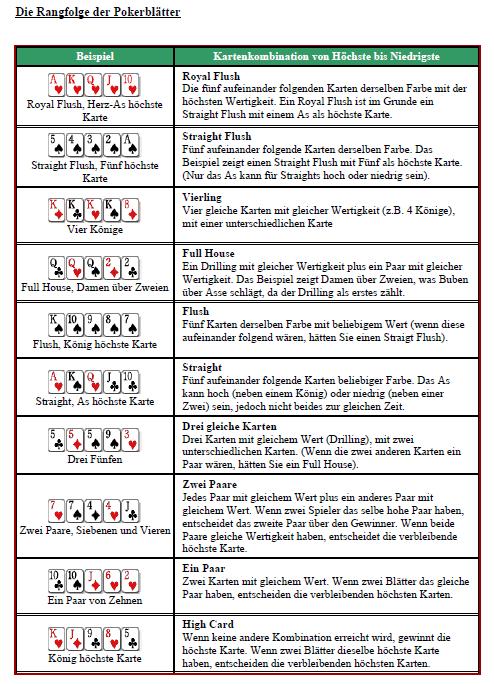
Each player still in the game at the end will determine the highest poker value among his own two cards and the five community cards. It is NOT a requirement that the player use both of his own cards. The player with the hand of highest poker value shall win. Following are the hand rankings.
- Straight flush: Five consecutive and suited cards. For example 5, 6, 7, 8, 9.
- Four of a kind: Four cards of the same rank, plus any fifth card. For example Q, Q, Q, Q ,4.
- Full house: Three of a kind and a pair. For example 6, 6, 6, J , J.
- Flush: Any five cards of the same suit, except for a higher ranking straight flush. For example A, Q, 8, 4 , 3.
- Straight: Five consecutive cards, except for a higher ranking straight flush. For example 8, 9, 10, J, Q.
- Three of a kind: Three cards of the same rank, plus any other two cards. For example 5, 5, 5, Q ,2 .
- Two pair: Two pairs, plus any fifth card. For example 8, 8, 2, 2 ,Q .
- Pair: A pair and any other three cards. For example 7, 7, 2, 5 ,A .
- ? High: Any five cards that do not form any higher poker hand. A king high hand for example might be K, Q, 7, 5 ,4 .
- If two or more players have poker values of the same rank then the individual cards will be used to break the tie. If necessary all five cards will be considered.
- I get asked a lot whether the two unused cards in a player's hand are used to break a tie. The answer is a firm NO. The two unused cards do not matter.
- If a new player arrives at the table he should either wait for the big blind position or put up an amount equal to the big blind, amounting to a call of the big blind.
- If a bet is made after another player runs out of money, then a separate pot is created. The player that ran out of money is not eligible to win the second pot. If more than one player runs out of money then multiple separate pots can be created.
- In formal games players may not bet with cash or buy chips with cash in the middle of a hand.
- There are numerous rules of etiquette, which I won't get into.
- There house may set the betting rules. There are three main types. A 'structured' game features raises of specified amounts. For example a '3/6 game' would mean that raises after the deal and flop are $3, and after the turn and river are $6. There is usually a limit to the number of raises a player may make, typically three. A 'pot limit' game has structured minimum raises but the maximum raise may be anything up to the amount in the pot at the time the raise is made. A 'no limit' game also has structured minimum raises but there is no maximum raise.
Examples
Example 1
Board: A, 2, 4, 5, 6
Player 1: J, 6
Player 2: 7, Q
Player 1 wins. Both have an ace high flush, so the second highest card is considered. Player 1's jack beats player 2's 7. The only way to have a flush tie is if the flush is entirely on the board and no hole cards are higher than the lowest card on the board in the same suit.
Example 2
Board: J, A, 7, 5, 6
Player 1: 2, J
Player 2: 10, J

Texas Hold'em Straight Odds
Player 2 wins. Both have a pair of jacks so the singletons are considered. High highet singleton in both hands is an ace so the second highest singleton is considered. Player 1's second highest singleton is a 7, compared to player 2's 10. A 10 beats a 7 so player 2 wins.
Example 3
Board: A, A, K, Q, J
Player 1: Q, J
Player 2: Q, 2
Tie. Both have a two pair of aces and queens, with a king singleton. Some people incorrectly believe that in such cases the unused cards are considered, in this case player 1's pair of jacks beating player 2's jack/2. Only the top five cards matter. The jacks and deuce are irrelevant.
One of the most important aspects of Texas Hold'em is the value of each two-card hand before the flop. The decision of how to play your first two cards is something you face every hand, and the value of your first two cards is highly correlated to your probability of winning.
The following table shows my power rating for each initial 2-card hand in a 10-player game. The numbers are on a 0 to 40 scale. Basically, you should only play hands that are dark green, blue, or purple. Of course you should be more be more liberal in late position and picky in early position. If forced I would say you should need 10 points in late position and 19 points in early position to call the big blind. If your table is loose, as if often the case online, you can play a bit looser yourself.
Use the top table if you have a pair, the middle table if your cards are suited, and the bottom table if your cards are unsuited. Except for a pair,look up your high card along the left and your low card along the top.
Following are the links to my tables of the value of each intial hand according to the number of players. The 10-player section explains the methodology for creating the table table.
Pot Odds
The following table shows the probability of making various hands after the flop and the correct 'pot odds.' The pot odds are the breakeven ratio of money in the pot to the amount you have to bet for the player to be indifferent about calling, assuming the player would definitely win if he makes the hand (a big if) and there are no additional bets (another big if). This table is a good starting point the player should make mental adjustments for the probability of winning without making the hand, losing with making the hand, and expected future bets. The odds of a two pair improving to a full house are the same as those for four to an inside straight.
Pot Odds — After Flop
| Hand | Probability of Making Hand | Pot Odds |
|---|---|---|
| Four to a flush | 34.97% | 1.86 |
| Four to an outside straight | 31.45% | 2.18 |
| Four to an inside straight | 16.47% | 5.07 |
The next table shows the pot odds after the turn.
Pot Odds — After Turn
| Hand | Probability of Making Hand | Pot Odds |
|---|---|---|
| 4 to a flush | 19.57% | 4.11 |
| 4 to an outside straight | 17.39% | 4.75 |
| 4 to an inside straight | 8.70% | 10.50 |
Hand Strength Calculator
I'm proud to present my new and improved Poker Odds Calculator. Enter any situation in Texas Hold 'Em, and it will tell you the probability of each possible outcome.
Poker Tournament Calculator
My Poker Tournament Calculator will determine each player's probability, for up to nine players, of finishing in each place, and his expected share of any prize pool, assuming equal skill among all players. It produces the same results as what is known as the Independent Chip Model.
Internal Links
- Pinapple — Strategy and analysis of which card to discard before the flop.
- Bad Beat Jackpots: What is the Probability of Hitting one?
- Texas Hold 'Em Dominated Hand Probabilities: What is the probability one of your opponents has similar, and better, hole cards than yours?
Written by:Michael Shackleford
Limit Texas Holdem Strategies And Advice
When playing Limit Texas Hold'em, striaght draws are good draws. When you frop a straight draw, it will either be an open-ened possible using both hole cards, open-ended possible using one hole card, or a gut-shot possible draw.
The way you play will depend on this. If you have an open-ened straight draw, you have eight outs which can improve your hand into a straight.
When the flop reveals a card that gives you an open-ended staight draw, there is about a 2.2 to 1, or 31-32%, change against an improvement on the turn or river.
If there is additional value in your hand, such as a pair or overcards, flush potential or other possibility, you're in an even better position. Let's say you hold the As-4s and on the flop you see 6d-5s-3h, you have eight outs for an open-ended straight draw, an overcard with three outs, a back-door flush draw with one out. This means that flop offers you a total of 12 outs, giving you a 45% chance of getting at least a pair. The more outs your hand offers, the better.
To draw or not draw?
If you flop a straight draw, it is better if the flop is a full rainbow. If the flop holds only two suits, you have to remove the flush potential outs. If the flop is two-suited and there is a great deal of action on that faop, you probably ought to fold your straight draw because someone is holding sets, two pairs or flush draws. Many times, when you flop an open-ended straight draw on a rainbow flop, you will have the right pot odds for the draw. But there are some exceptions you should know about:
1. If the flop shows a pair and there is a lot of heavy action on that flop. With board pairs, it is too easy for the other players to create full houses.
2. If you are playing heads-up and do not have a pair or two overcards at the flop, the pot will not give you good enough odds to call. Of course, you could try a semi-bluff at that point, but do not check and call all the way to the river unless you have hit your draw.
When drawing to an open-ended straight, be certain you are not drawing to the low end. If you have 5s-4s and the flop shows Js-7h-6c, you are have an open-ended straight draw, with both ends having outs. However, play it like a gut-shot draw with only four outs since you will only feel comfortable if a 3 hits.
Open-Ended Straight Draws Using Only One Card from your Hand
If you have to use only one hole card and the flop to create your straight draw, it is not nearly as b as if you were using two hole cards. This is because the straight possibility is clear to all your opponents and they might already hold a straight as a result of the same flop! There is a much better possiblity you'll end up splitting the pot if you do make the straight. The action will potentially decline when the fourth straight card hits the table and it could be difficult to build a pot even if you do have the winning hand.
Gut-shot Straight Draws
With this type of draw, there is only one card that gives you the straight, making a total of four outs. That means it is 11-1 against improving your hand at the turn. This hand is pretty b only when it has two overcards or other additional values. If you hold Ks-Qs on the flop of Ts-9c-6d, you have a reasonably b draw. The gut-shot draw to the nuts, which means the four outs, two overcards with six outs (but watch out if a Q hits because of the possible straight) and back-door flush possibility with one out gives you enough options to play this hand with some aggression.
In general, you will not get sufficient pot odds to draw with gut-shot straight draws except when the pot has been raised pre-flop. If there are lots of callers before the flop and on the flop it would be correct to draw, only do so if you are drawing to the nut straight. If you raise with a hand of Aqs, and four players call, if the flop comes as K-T-3, there will be 10 small bets in the pot. If you check, the player behind you bets and few call in between, the pot odds warrant a call in hopes of hitting that J that would be the nut straight. You hold about 11-1 against on the turn, meaning 9.7%, but the pot is large enough to warranty this call. When drawyhing to gut-shot straights, however, you should always fold if someone might raise behind you.
Strategy Article 1.Limit Holdem Playing Flops
Texas Holdem Tournament Videos
Strategy Article 2. Limit Holdem Starting Hands
Texas Hold'em Straight Vs Flush
Strategy Article 3. Limit Holdem - Playing Middle or Bottom Pairs on the Flop
Texas Hold'em Straight Tie
Strategy Article 4. Limit Holdem Overcards Flop